India remains world’s largest importer of arms: SIPRI report
- According to Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), India is the world’s largest arms importer for the five-year period during 2018-22 .
- However, India’s arms imports have dropped by 11% between 2013–17 and 2018–22.
Top Arms Suppliers to India
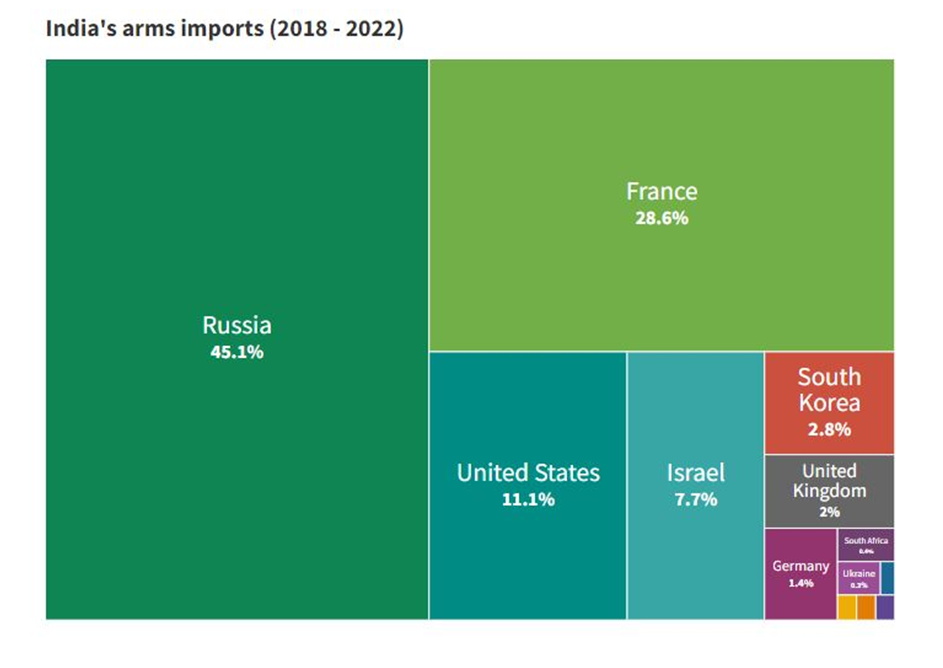
Arms import by Country
- For the same period, India remained the largest arms importer followed by Saudi Arabia.
- Russia accounted for 45% of India’s imports followed by France (29%) and the US (11%).
- India was the third largest arms supplier to Myanmar after Russia and China, accounting for 14% of its imports.
Reasons for India’s Arms Imports
- Complexities with neighbourhood: India’s tensions with Pakistan and China largely drive its demand for arms imports. With an 11% share of total global arms imports, India was the world’s biggest importer of major arms in 2018–22,”.
- Procurement bottlenecks: India’s slow and complex arms procurement process, efforts to diversify its arms suppliers, and attempts to replace imports with major arms that are designed and produced domestically have contributed to the decrease in arms imports.
Russia’s position as India’s Main Arms Supplier
- India diversifying its imports: Russia’s position as India’s main arms supplier is under pressure due to strong competition from other supplier states.
- Self-arming for ongoing war: This is due to increased Indian arms production, and constraints on Russia’s arms exports related to its invasion of Ukraine.
Global Arms Transfers
- Arms imports by Pakistan increased by 14% between 2013–17 and 2018–22 and accounted for 3.7% of the global total with China supplying 77% of Pakistan’s arms imports in 2018–22.
- While the global level of international arms transfers decreased by 5.1%, imports of major arms by European states increased by 47% between 2013–17 and 2018–22 in the backdrop of the war in Ukraine.
- The U.S. share of global arms exports increased from 33% to 40% while Russia’s fell from 22% to 16%.
What we can conclude from this?
- Security concerns: India’s tensions with neighboring countries such as Pakistan and China, which have led to security concerns and a perceived need for a strong military.
- Slow and complex procurement process: India’s procurement process for arms is often slow and complex, leading to delays in acquiring weapons and equipment.
- Lack of domestic production: India’s domestic arms production capabilities are still limited, which makes it difficult for the country to produce high-tech weapons and equipment.
- Diversification of suppliers: While Russia has been the traditional supplier of arms to India, in recent years India has been diversifying its sources of weapons and equipment to countries such as France, Israel, and the United States.

